7.11 EMP_mutate
The EMP_mutate module is highly versatile, allowing transformations not only based on assay, rowdata, and coldata of a dataset, but also on the results of data analysis. To help users better understand its usage, the basic parameters of the module are described below:
- obj : Specifies the input object, which can be an MAE or EMPT.
- experiment : Specifies the name of the omics assay to analyze (character).
- ... :Inherited from the dplyr::mutate() function, supporting a variety of data transformations.
- .by : Inherited from
dplyr::mutate(); equivalent to performinggroup_by()before the transformation. - .before : Inherited from
dplyr::mutate(); sets the position of the new column to be placed before a specified column. - .after : Inherited from
dplyr::mutate(); sets the position of the new column to be placed after a specified column. - mutate_by: Specifies whether the transformation is applied by
sampleor byfeature. - location:Defines where the new column is created — in
assay,rowdata, orcoldata. - action: A character string selecting between
"colwise"and"rowwise", indicating whether the operation should be performed column-wise or row-wise. - keep_result: If the input is TRUE, it means to keep all analysis results, regardless of how samples and features change. If the input is a name, it means to keep the corresponding analysis results.
7.11.1 Mutate for the MultiAssayExperiment
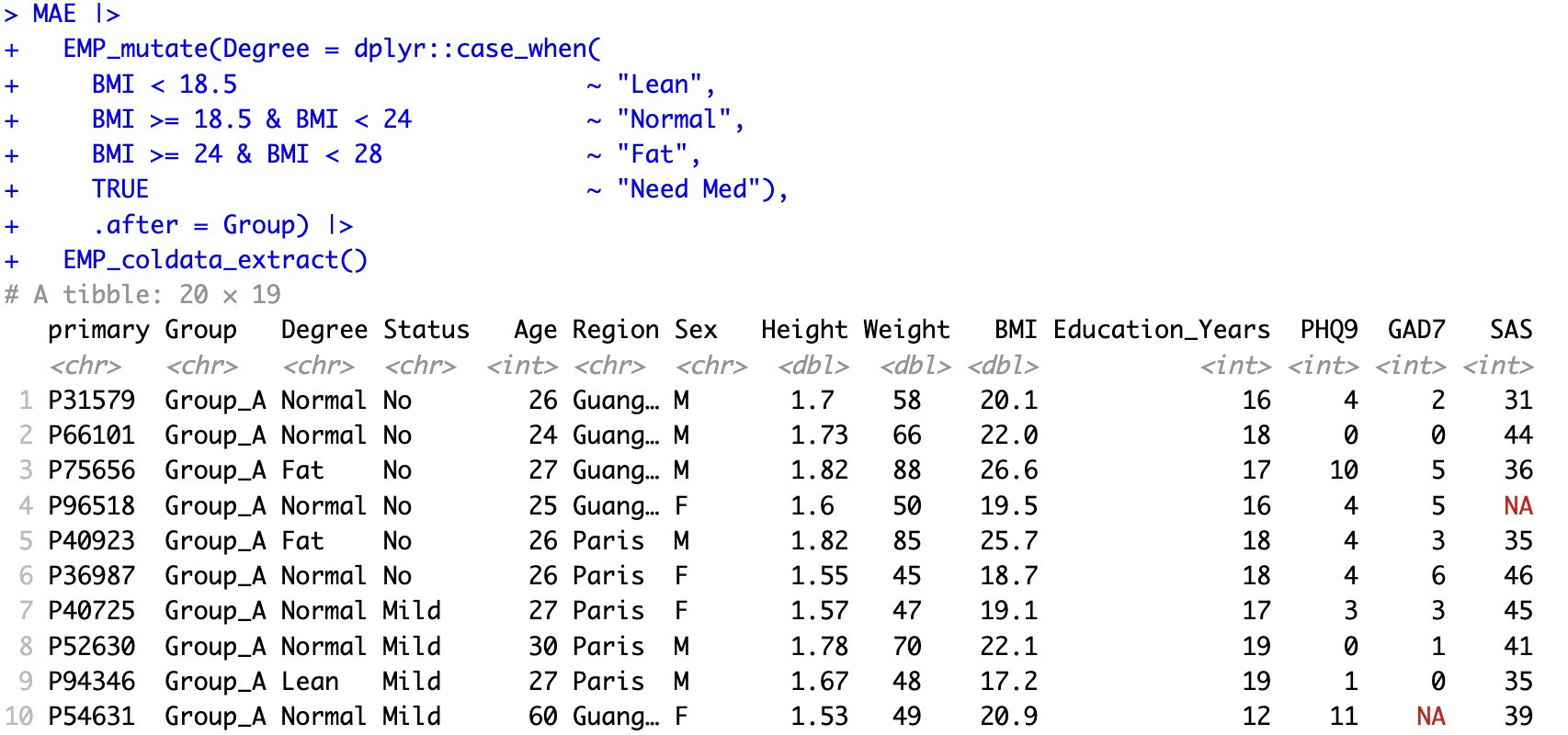
🏷️Example: Create a new group.
MAE |>
EMP_mutate(Degree = dplyr::case_when(
BMI < 18.5 ~ "Lean",
BMI >= 18.5 & BMI < 24 ~ "Normal",
BMI >= 24 & BMI < 28 ~ "Fat",
TRUE ~ "Need Med"),
.after = Group)
After mutating, users can use the module EMP_coldata_extract to observe the result.
MAE |>
EMP_mutate(Degree = dplyr::case_when(
BMI < 18.5 ~ "Lean",
BMI >= 18.5 & BMI < 24 ~ "Normal",
BMI >= 24 & BMI < 28 ~ "Fat",
TRUE ~ "Need Med"),
.after = Group) |>
EMP_coldata_extract()
7.11.2 Mutate for the signle omics data
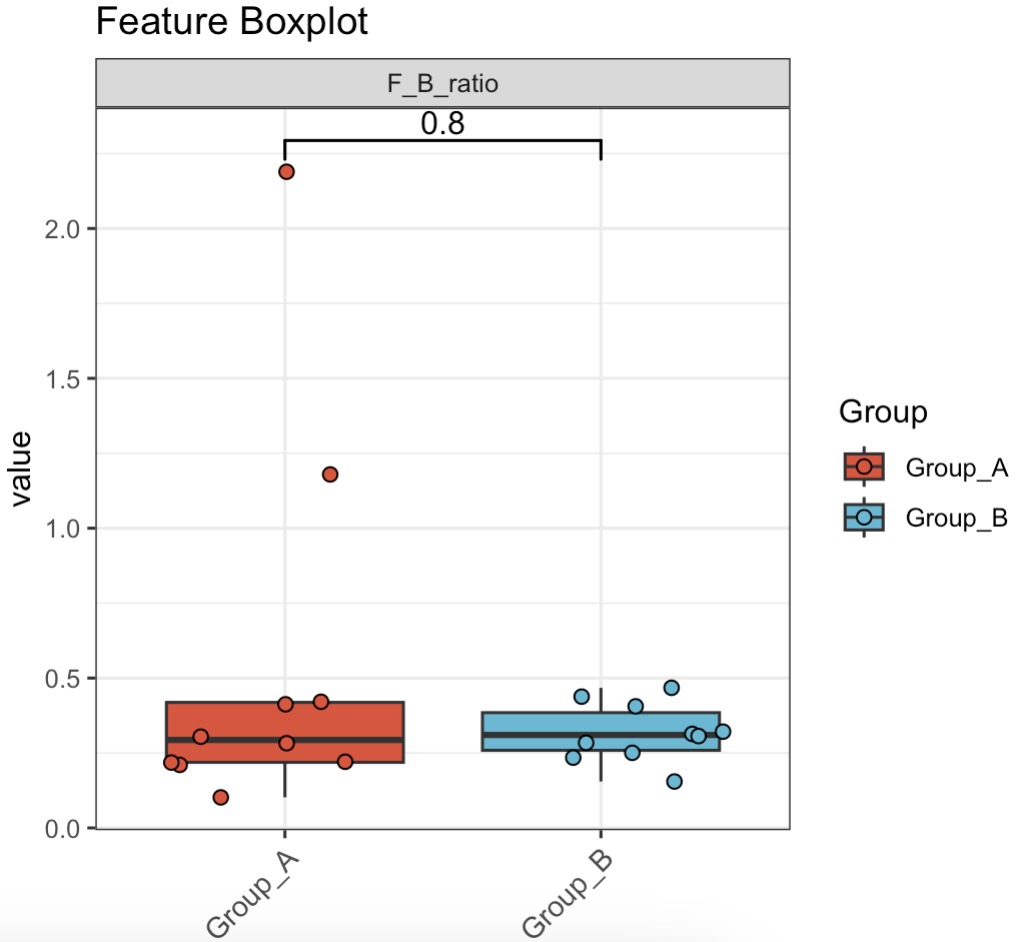
🏷️Example1: Compute the Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio.
MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_collapse(collapse_by = 'row',estimate_group = 'Phylum') |>
EMP_mutate(F_B_ratio = Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes,
.by = primary,.before = 2,
mutate_by = 'sample',location ='assay') |>
EMP_filter(filterFeature = 'F_B_ratio') |>
EMP_boxplot(estimate_group='Group')
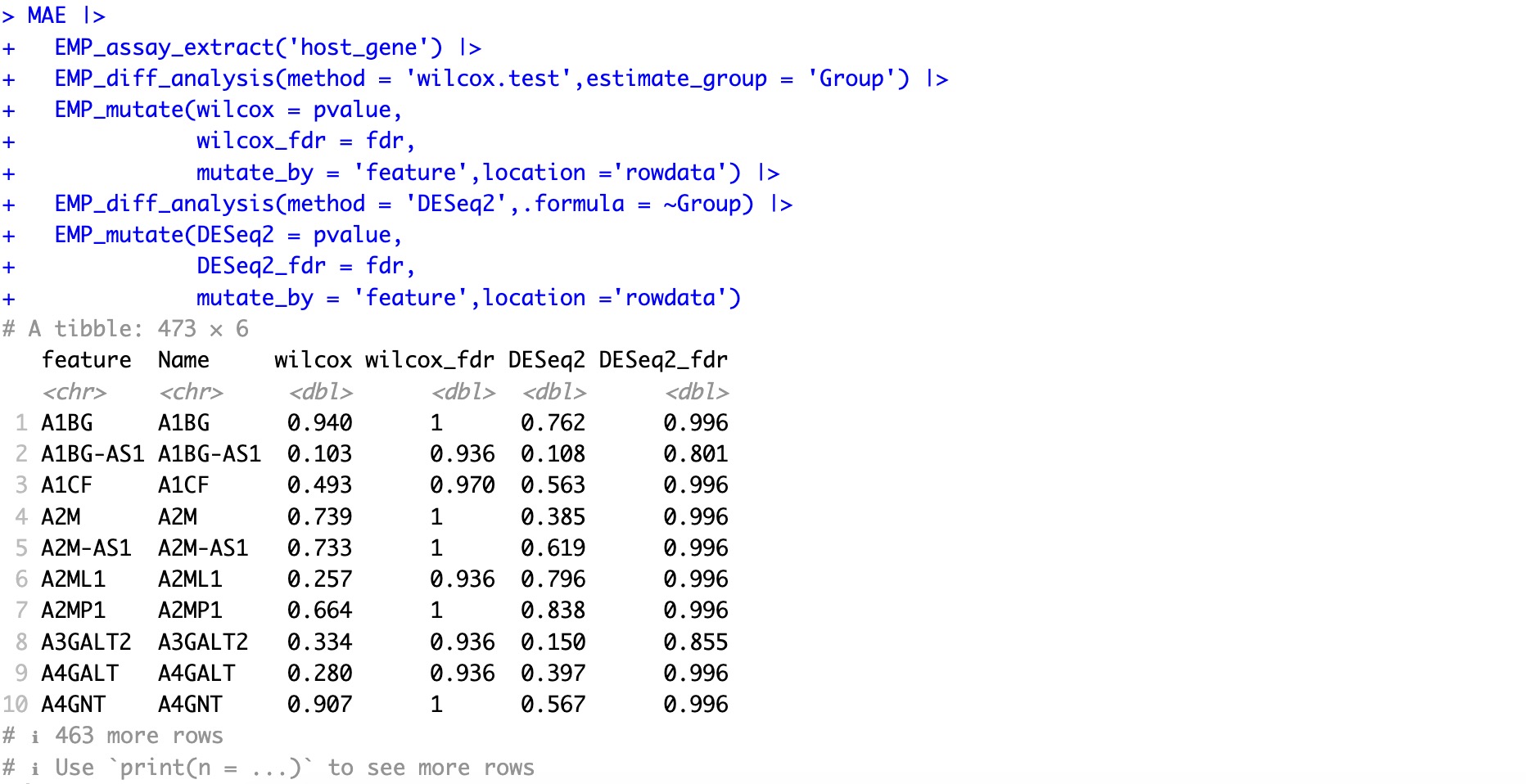
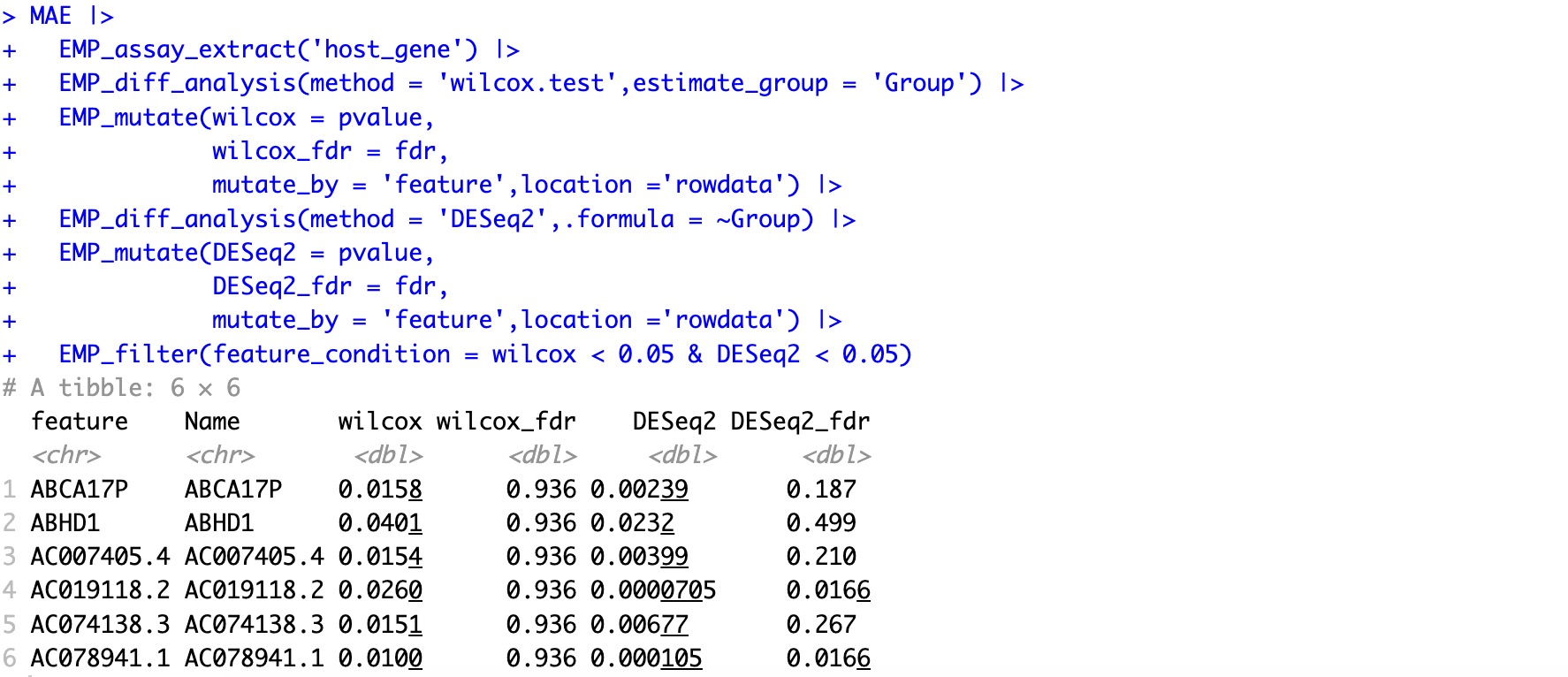
🏷️Example2:This process integrates results from multiple differential analysis algorithms and adds annotation information to the features.
MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('host_gene') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method = 'wilcox.test',estimate_group = 'Group') |>
EMP_mutate(wilcox = pvalue,
wilcox_fdr = fdr,
mutate_by = 'feature',location ='rowdata') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method = 'DESeq2',.formula = ~Group) |>
EMP_mutate(DESeq2 = pvalue,
DESeq2_fdr = fdr,
mutate_by = 'feature',location ='rowdata')
This allows us to identify feature genes that are significant in both differential analysis methods.
MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('host_gene') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method = 'wilcox.test',estimate_group = 'Group') |>
EMP_mutate(wilcox = pvalue,
wilcox_fdr = fdr,
mutate_by = 'feature',location ='rowdata') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method = 'DESeq2',.formula = ~Group) |>
EMP_mutate(DESeq2 = pvalue,
DESeq2_fdr = fdr,
mutate_by = 'feature',location ='rowdata') |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = wilcox < 0.05 & DESeq2 < 0.05)
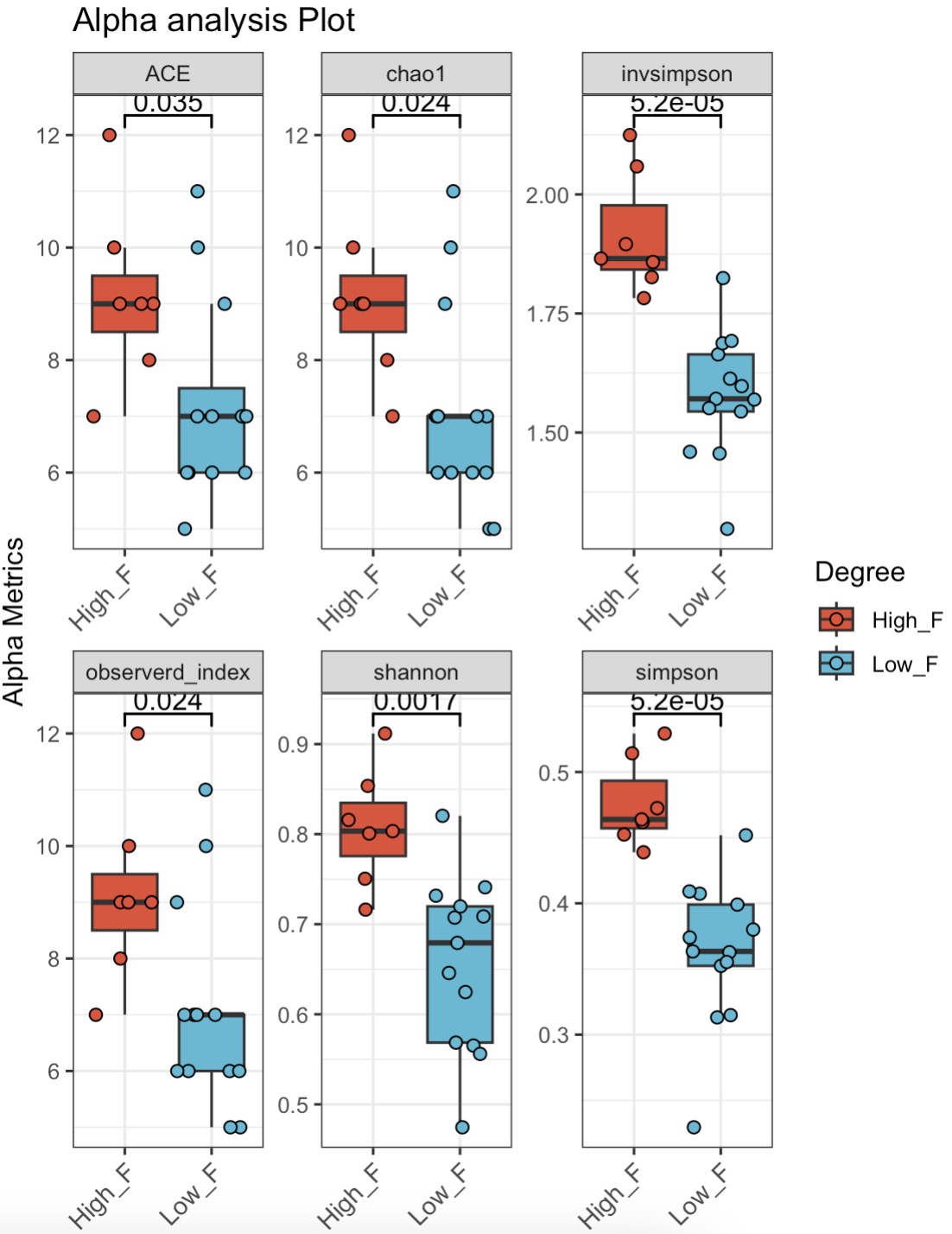
🏷️Example3:Grouped by Firmicutes abundance levels and compared for alpha diversity.
MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_decostand(method = 'relative') |>
EMP_collapse(collapse_by = 'row',estimate_group = 'Phylum') |>
EMP_mutate(Degree = dplyr::case_when(
Firmicutes >= mean(Firmicutes) ~ "High_F",
Firmicutes < mean(Firmicutes) ~ "Low_F"),
.after = Group) |>
EMP_alpha_analysis() |>
EMP_boxplot(estimate_group='Degree')